What is a variable?
A variable is a container that stores a meaningful value that can be used throughout a program. For example one variable that stores the regular price of an item for calculating tax on it. Variables store this information in a computer's memory and the value of a variable can change all through out a program.Declaring variables
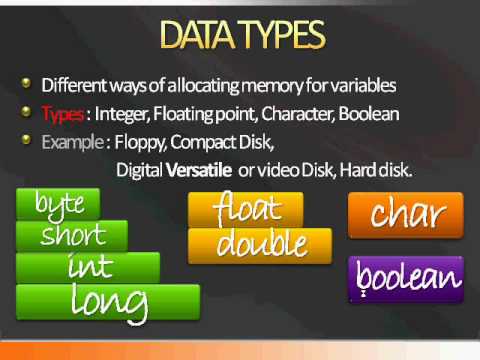
Use these keywords when declaring your variables to set the data type of the variable.| Keyword | Type of data the variable will store | Size in memory |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | true/false value | 1 bit |
| byte | byte size integer | 8 bits |
| char | a single character | 16 bits |
| double | double precision floating point decimal number | 64 bits |
| float | single precision floating point decimal number | 32 bits |
| int | a whole number | 32 bits |
| long | a whole number (used for long numbers) | 64 bits |
| short | a whole number (used for short numbers) | 16 bits |
Example:
char aCharacter; int aNumber;
Example:
char aCharacter = 'a'; int aNumber = 10;
Declaring a variable and then giving it a value:
char aCharacter; aCharacter = 'a'; int aNumber; aNumber = 10;
NOTE: A variable must be declared with a data type or an error will be generated!
Naming variables
Rules that must be followed when naming variables or errors will be generated and your program will not work:
- No spaces in variable names
- No special symbols in variable names such as !@#%^&*
- Variable names can only contain letters, numbers, and the underscore ( _ ) symbol
- Variable names can not start with numbers, only letters or the underscore ( _ ) symbol (but variable names can contain numbers)
via [landofcode.com]







0 comments:
Post a Comment